What is Diabetes Pregnancy (Gestational Diabetes)
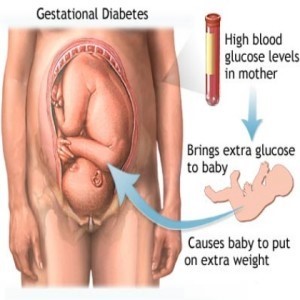
Understanding Diabetes Pregnancy Gestational diabetes is a condition of a pregnant woman who had blood glucose levels are higher than normal first diagnosed during pregnancy. Only 2 to 10 percent of pregnant women with gestational diabetes. Causes of Diabetes Pregnancy By the time a woman is pregnant, changes in hormones in the body makes insulin becomes ineffective. Because insulin helps the absorption of glucose by the body's cells are not effective, consequently the amount of glucose in the blood increases.
Pregnancy Diabetes Risk Factors
• Have a history of diabetes in the family
• Being overweight before pregnancy • Never give birth to large babies (more than 4.5 kg)
• Have high blood pressure
• Never give birth defects or death Symptoms of Diabetes Pregnancy Gestational diabetes usually have no symptoms, even if no symptoms are not dangerous for pregnant women. Blood glucose levels usually return to normal after delivery.
Symptoms that may arise include:
• Sluggish
• Nausea and vomiting
Pregnant women should undergo an oral glucose tolerance test (oral glucose tolerance test) between week 24 to week 28 to check their blood glucose levels. Women who are at risk of diabetes blood glucose should be checked early.
• Weight loss
• Frequent thirst
• Frequent urination Pregnancy Diabetes Diagnosis Pregnancy diabetes usually starts since entering half of pregnancy.
Pregnant women should undergo an oral glucose tolerance test (oral glucose tolerance test) between week 24 to week 28 to check their blood glucose levels. Women who are at risk of diabetes blood glucose should be checked early.
Diabetes Complications of Pregnancy Diabetes in pregnancy can affect the health of mother and baby.
Some complications of gestational diabetes include:
• Childbirth large babies (probably need a cesarean)
• The mother may have type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes later in life
• Children at risk of developing diabetes later in life
• Risk of deformed babies or infants died at birth
• Infants experience hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) some time after birth.
Diabetes Care Pregnancy The purpose of gestational diabetes treatment is to lower blood glucose levels to within normal limits, and ensure the health of the unborn baby.
Treatment of gestational diabetes, among others
• Eat a healthy balanced diet recommended by the gynecologist
• Exercise regularly
• Get medical treatment including insulin if necessary Pregnancy Diabetes Prevention Gestational diabetes is detected early in pregnancy may reduce the risk of complications for the mother naupun baby.
Pregnancy check regularly Checking blood glucose early in pregnancy and at week 24 to week 28. If the mother is overweight before pregnancy, first reduce weight before pregnancy.